Information Center
Welcome to our Information Center
PEOPLE DON’T PLAN TO FAIL, THEY JUST FAIL TO PLAN, THEN SOME FAIL TO FOLLOW THE PLAN! DON’T ALLOW THIS TO HAPPEN!
We hope your visit will help you understand the opportunities and potential rewards that are available when you take a proactive approach to your personal financial situation. LET-US-SEE FG created this website to help you gain a better understanding of financial concepts behind Credit Repair, Debt Elimination, Financial Education (financial literacy), Insurance Products, Retirement/Tax Strategies*, and overall Wealth Preservation. Most importantly, we hope you see the value of working with skilled professionals to pursue your financial success. Example:
A Closer Look at Our Services
The financial management process at LET-US-SEE FG begins with an in-depth evaluation of your current financial situation. Once we’ve established your overall objectives, we’ll focus on your specific goals. With changing economic conditions and market swings, we advocate saving and investing consistently over the long run, eliminating debt while maintaining an adequate level of income protection (life insurance coverage). We work with you side by side so that you’re confident with the financial suggestions we make.
Some other Services LUSFG Offer:
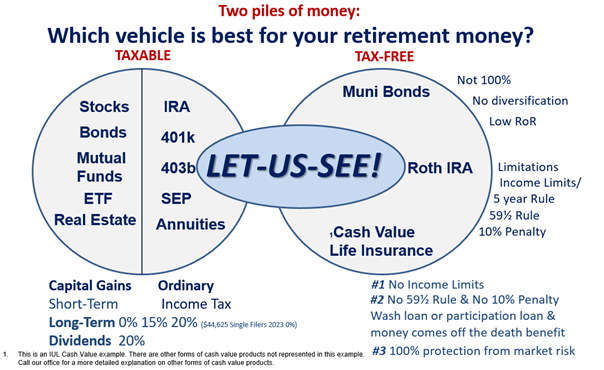
- Retirement Planning (FIN), also see: (Investment Terms, Qualified Plans & Rules)
- Debt Elimination (DFD)
- DIY Credit Repair System (goal 750-850 score)
- Cash flow/Expense Management
- Tax Strategies for Employees and the Self-Employed*
LUSFG don’t give tax or estate planning advice, please consult your personal tax & estate professional
Investment Vehicles Terms
- Stocks Are share in the ownership of a corporation and represents a claim on the company’s assets and earning. As you require more stock, your ownership stake in the company becomes greater.
- Bonds Are a long-term debt instrument. When companies or other entities need to raise money to finance new projects, maintain ongoing operations, or finance existing other debts, they may issue bonds directly to investors instead of obtaining loans from a bank.
- Real Estate Is property consisting of land and the buildings on it, along with its natural resources such as crops, minerals or water. Immovable property of this nature; with an interest vested in this item of real property, (more generally) buildings or housing in general.
- Mutual Fund A company that pools investors’ money and invests in a variety of investments.
- ETF’s Having some characteristics of mutual funds, but are traded throughout the day, similar to individual stocks. They are comprised of stock, bonds or other assets.
- Cryptocurrency A digital currency in which transactions are verified and records maintained by a decentralized system using cryptography, rather than by a centralized authority. Decentralized cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin now provide an outlet for personal wealth that is beyond restriction and confiscation.
- Deferred Annuities Deferred annuities have two phases: accumulation, where you earn interest on your investment, followed by the distribution phase, when the account is annuitized. The investment gains are tax-deferred until you begin taking withdrawals.
- Immediate Annuities Immediate annuities have no accumulation period. Buyers plunk down their payments and go straight to the distribution phase. An immediate annuity guarantees you a set amount of income for life — or for your and your spouse’s life.
- Fixed Annuities A fixed annuity earns a fixed rate during the accumulation stage. Generally, the interest rate is agreed upon for the first year and then is reset in subsequent years based on market conditions. But investors can find annuities with a set interest rate that lasts for a number of years. During the distribution period, fixed annuities are regular fixed payments that don’t change in amount.
- Variable Annuities The payout from a variable annuity will be based on its underlying investments, called sub-accounts. These accounts fluctuate in value. “Variable annuities are really a lot like tax-deferred mutual funds — you put money in, you select the funds, and you hope over time that it grows.
Qualified Plans Options
- 401 (K) – A pension plan used by private-sector businesses; provides either tax deductions, tax deferrals or both. Employers may also elect to match contributions made to the plan up to a percentage of one’s income.
- 403 (B) – (Also called a tax sheltered annuity or TSA plan) is a pension plan used by public-sector and certain 501(c)(3) tax-exempt organizations. Employees save for retirement by contributing to individual accounts. Employers can also contribute to employees’ accounts.
- Traditional IRA – Contributions are tax-deductible (often simplified as “money is deposited before tax” or “contributions are made with pre-tax assets”), all transactions and earning within the IRA have no tax impact, and withdrawals at retirement are taxed as income (except for those portions of the withdrawal corresponding to contributions that were not deducted).
- Roth IRA – Contributions are made with after- tax assets, all transactions within the Roth IRA have no tax impact, and withdrawals are usually tax-free. No required minimum distributions (RMDs) from the original owner at 73 (in 2023). Named from Senator William V. Roth, Jr., the Roth IRA was introduced as part of the Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997.
- SIMPLE IRA – (Saving Incentive Match Plan for Employees) Established for employers with 100 or fewer employees, including self-employed individuals that requires employer matching contributions to the plan (3% matching or 2% non-elective contribution) whenever an employee makes a contribution. Employee must have made $5,000 in the preceding year.
- SEP IRA – A provision the allows an employer (typically a small business or self-employed individual) to make retirement plan contributions into a Traditional IRA established in the employee’s name, instead of to a pension fund in the company’s name.
- Rollover IRA – No real difference in tax treatment from a traditional IRA, but the funds come from a qualified plan or 401(k) – 403(b) account and are “rolled over” into the rollover IRA instead of contributed as cash. No other assets are commingled with these rollover amounts.
- Keogh Plan – Is a retirement plan for the self-employed or unincorporated small business. They are generally defined contribution plans or defined benefit plans. Keogh plan can invest in the same instruments as other types of retirement plans, such as stocks, bonds, certificates of deposit (CD’s), and annuities.
Qualified Plans Have Two Rules
- 59½ – If you take money out of a retirement plan such as a IRA, 401(K), or 403(B) etc. before the age of 59½ you will have a penalty to pay. The penalty is 10% plus the money is taxable at your current tax rate.
- 73 – Required Minimum Distribution (“RMD”) begin at age 73 (2023) from qualified retirement account unless it is a Roth IRA which is exempted from the rule. If you do not take out your RMD when you turn 73, the IRS imposes a penalty of 25%. Example: if you were supposed to take out $4,000 and you did not, you would be assessed a penalty of $1,000. See: SECURE ACT 2.0 changes!
- Defined Benefit Plans – Are different and can be discussed at our one on one meeting.
